Comparative and superlative adverbs
Comparison (-er/-est)
| Comparative ending in -er | Superlative ending in -est | |
|---|---|---|
| one-syllable adverbs (hard) | harder | hardest |
| adverbs with the same form as adjectives (early) | earlier | earliest |
Comparison (more / most)
| Comparative formed with more | Superlative formed with most | |
|---|---|---|
| adverbs ending in -ly (happily) | more happily | most happily |
Irregular comparisons
| positive form | comparative | superlative | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| well | better | best | ||
| badly | worse | worst | ||
| ill | worse | worst | ||
| little | less | least | ||
| much | more | most | ||
| far (place + time) | further | furthest | ||
| far (place) | farther | farthest | ||
| late (time) | later | latest |
Adverb - superlative:
incorrect - She is the most fastest runner.
correct - She is the fastest runner.
(She is either the fastest runner or she is not, she cannot be the most fastest.)
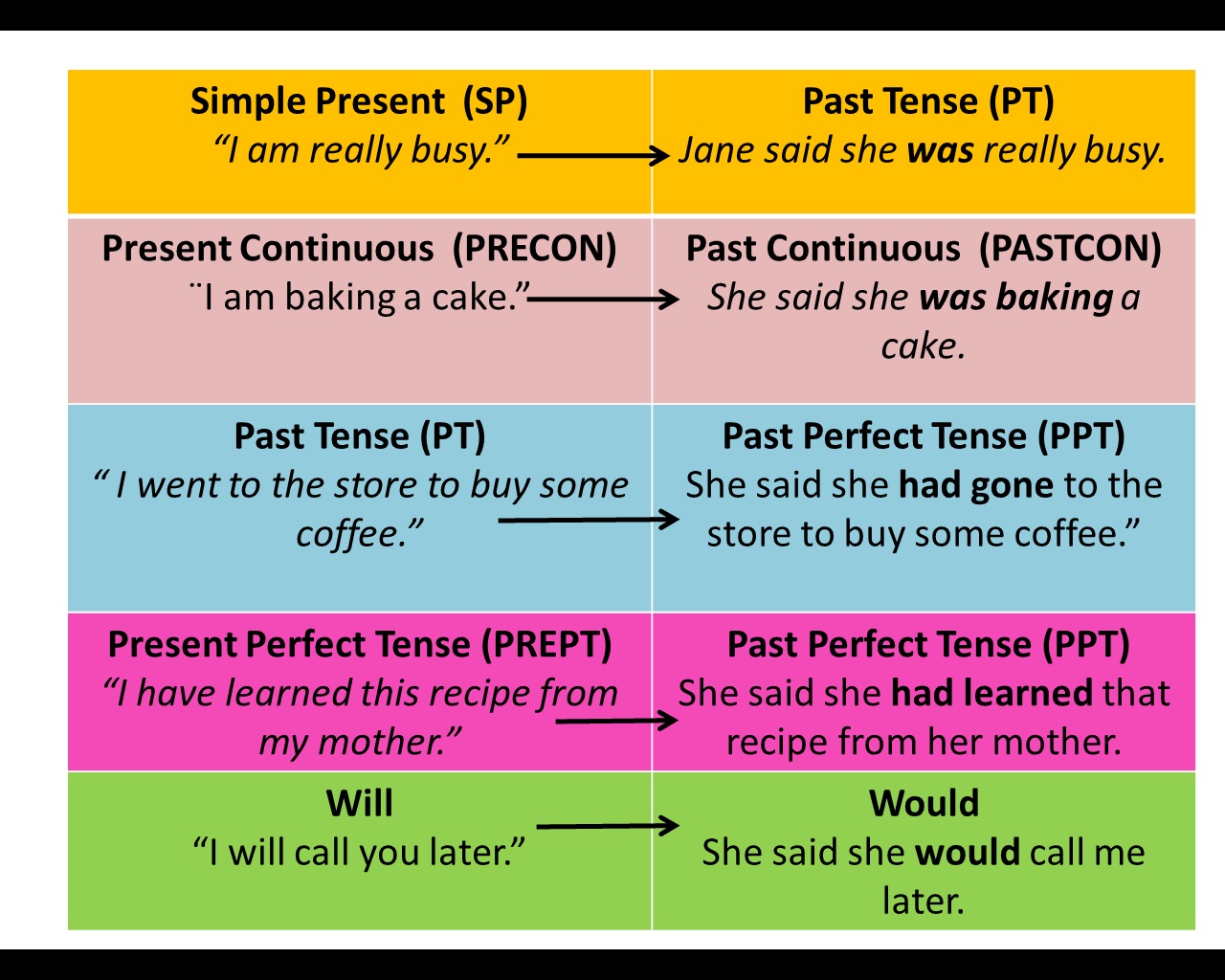
Reported speech

Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. (Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell'.) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: “I like ice cream”.
- Reported speech: She says she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'.
But, if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Direct speech: “I like ice cream”.
- Reported speech: She said she liked ice cream.
| Tense | Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|---|
| present simple | “I like ice cream” | She said (that) she liked ice cream. |
| present continuous | “I am living in London” | She said she was living in London. |
| past simple | “I bought a car” | She said she had bought a car OR She said she bought a car. |
| past continuous | “I was walking along the street” | She said she had been walking along the street. |
| present perfect | “I haven't seen Julie” | She said she hadn't seen Julie. |
| past perfect* | “I had taken English lessons before” | She said she had taken English lessons before. |
| will | “I'll see you later” | She said she would see me later. |
| would* | “I would help, but..” | She said she would help but... |
| can | “I can speak perfect English” | She said she could speak perfect English. |
| could* | “I could swim when I was four” | She said she could swim when she was four. |
| shall | “I shall come later” | She said she would come later. |
| should* | “I should call my mother” | She said she should call her mother |
| might* | "I might be late" | She said she might be late |
| must | "I must study at the weekend" | She said she must study at the weekend OR She said she had to study at the weekend |
* doesn't change.

No comments:
Post a Comment